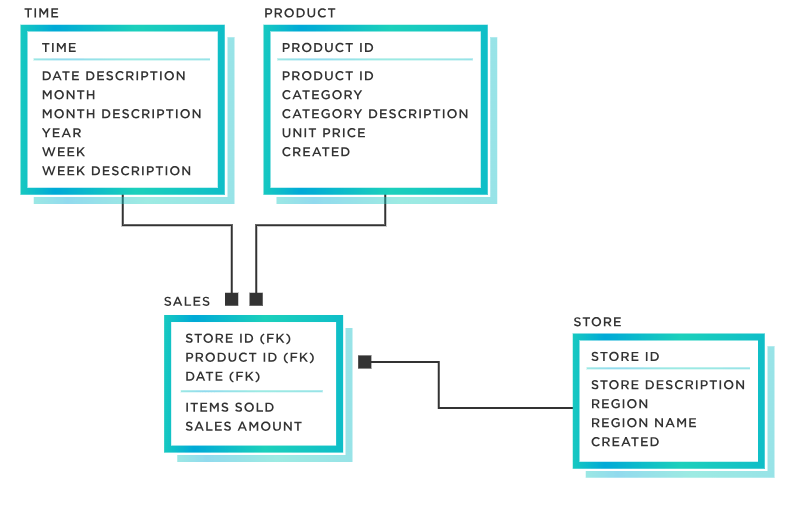
Data modelling is an essential step in the data analytics process, that enables data analysts to identify and represent data structures, relationships, and patterns. To accomplish this, various data modelling tools are available, each with its strengths and capabilities.
In this guide, we’ll provide an overview of some popular data modelling tools, comparing their features, use cases, and advantages to help you make an informed choice for your next data analytics projects.
Understanding Data Modeling Tools
Data modelling tools are software applications that facilitate the process of creating, visualizing, and managing data models. These tools help data analysts and engineers design databases, define relationships between entities, and ensure data integrity.
They often provide a graphical interface that users can use to build and modify data models by dragging and dropping entities, attributes, and relationships. Additionally, data modelling tools often offer features such as data validation, reverse engineering, and forward engineering to help users ensure the accuracy and consistency of their data models. By simplifying the data modelling process, these tools enable organizations to optimize their database structures and improve data management practices.
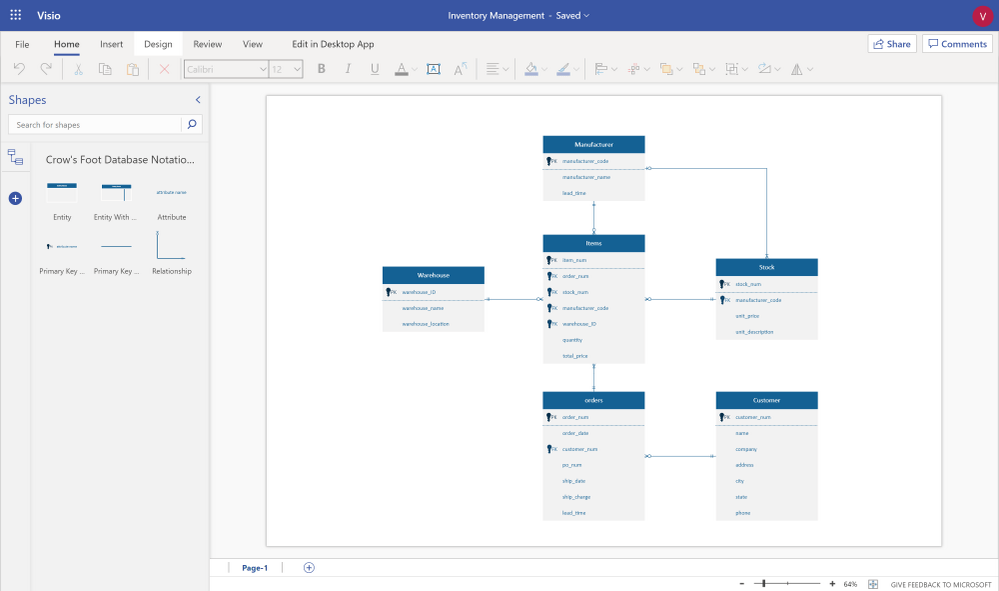
1. Microsoft Visio
Key Features:
- Intuitive drag-and-drop interface: With its intuitive drag-and-drop interface, Microsoft Visio makes it effortless to create professional-looking models of your data.
- Extensive template library for various data modelling types: This includes process flowcharts, network diagrams, and even floor plans. With Visio’s extensive template library, users can easily find the perfect design for their specific data modelling needs.
- Integration with other Microsoft products: Visio seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products, such as PowerPoint and Excel, allowing users to easily import and manipulate data from these applications.
Use Cases:
- Business process modelling: Visio is a popular tool for business process modelling, enabling users to visually represent and analyze complex workflows and procedures, identifying areas for improvement.
- Entity-relationship diagrams: Visio enables the creation of entity-relationship diagrams. These are crucial for understanding relationships within a database and enhancing database design and optimization.
- UML diagrams: Visio’s UML diagramming capabilities enable users to create various types of diagrams. These aid in the design, development, and maintenance of complex software systems.
Advantages:
- Familiar interface for users of other Microsoft products.
- Supports a wide range of diagram types.
2. Erwin Data Modeler
Key Features:
- Robust data modelling capabilities: Erwin Data Modeler offers a comprehensive set of tools and features for effective data modelling. It allows users to create, design, and document database structures with ease.
- Forward and reverse engineering for databases: Erwin Data Modeler offers forward engineering for SQL script generation and reverse engineering for extracting existing database structures for comprehensive data models.
- Data governance and metadata management: The tool enables users to establish and enforce data governance policies, ensuring data quality, compliance, and security, and facilitates centralized metadata management across the organization.
Use Cases:
- Database design and optimization: The tool provides database design and optimization capabilities, allowing users to create efficient and well-structured databases.
- Data governance and compliance: With robust data governance and metadata management, users can ensure that the database design follows best practices and meets data quality and security requirements.
Advantages:
- Comprehensive data governance features.
- Strong support for large-scale, enterprise-level data modelling.
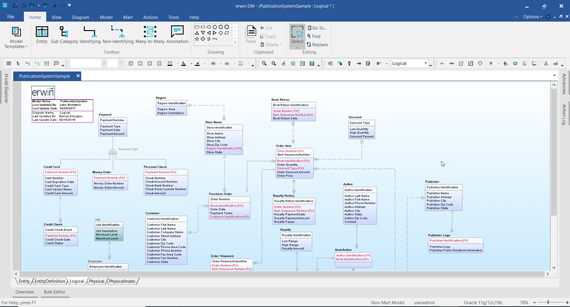
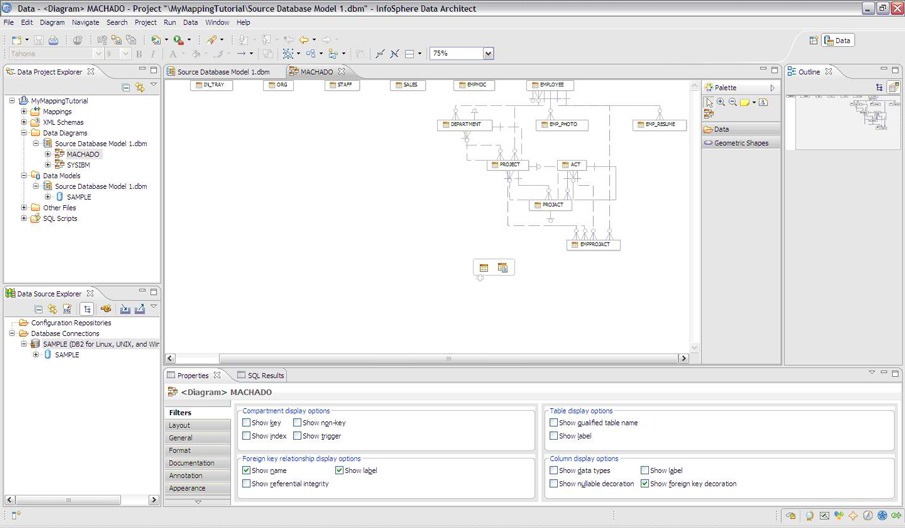
3. IBM InfoSphere Data Architect
Key Features:
- Visual data modelling with forward and reverse engineering: This feature streamlines the design process and ensures that the final product accurately represents the intended data architecture.
- Integration with IBM’s data management ecosystem: This integration enables users to leverage additional functionalities such as data governance, data quality management, and data integration. This enhances the overall data management experience.
- Data lineage and impact analysis: This functionality allows users to trace the origin of data elements, understand how they are transformed and manipulated throughout the data management lifecycle, and identify the impact of any changes made to the data.
Use Cases:
- Enterprise data modelling: Data modelers design and maintain enterprise data structures by understanding data lineage, identifying dependencies, and relationships between data elements, and ensuring accuracy and integrity.
- Data governance and compliance: By implementing proper data governance practices, organizations can establish guidelines and processes for data usage, access, and security. This helps ensure that data is handled in a consistent and compliant manner, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
Advantages:
- Seamless integration with IBM’s data management solutions.
- Strong capabilities for data lineage and impact analysis.
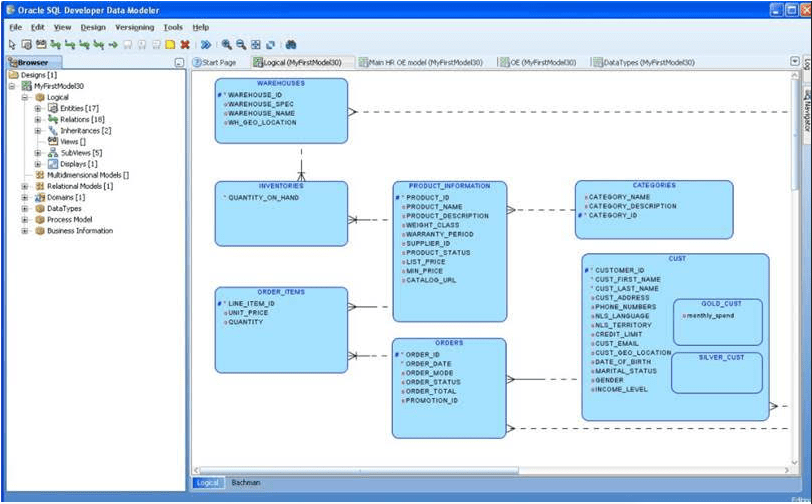
4. Oracle SQL Developer Data Modeler
Key Features:
- Intuitive interface with advanced visualization options: Oracle SQL Developer Data Modeler offers an intuitive interface for easy data model manipulation and advanced visualization options for detailed diagrams and database structures.
- Support for various modelling notations (Barker, IDEF1X, etc.): Oracle SQL Developer Data Modeler offers users customizable notation and features like generating SQL scripts for database creation and modification, saving time and effort.
- Integrated reporting and documentation. Users can generate detailed reports and documentation of their data models, making it easier to share and communicate the design with stakeholders.
Use Cases:
- Designing Oracle databases: This tool enables users to create and modify database structures and define tables, columns, constraints, and relationships, with a visually appealing interface for easy modification.
- Data modelling for Oracle-based applications: Developers can accurately represent the structure and relationships of data in an Oracle database. This enables them to design robust and scalable applications that can handle large amounts of data and complex operations.
Advantages:
- Native integration with Oracle Database.
- Extensive reporting and documentation features.
5. Lucidchart
Key Features:
- Cloud-based, collaborative platform: Being cloud-based, Lucidchart ensures that all changes are automatically saved and accessible from any device with an internet connection. Additionally, due to its collaborative features, multiple users can work on the same diagram simultaneously, making it easy to share ideas and streamline communication within a team.
- Support for various diagram types: Support for various diagram types allows users to visually represent complex data structures and relationships. This feature enables teams to effectively analyze and communicate data-driven insights, enhancing decision-making processes.
- Integration with popular cloud storage services: Lucidchart integrates with popular cloud storage services like Google Drive and Dropbox. This makes it easy to share files and collaborate with team members across different locations.
Use Cases:
- Collaborative data modelling and diagramming: This allows team members to work together in real-time to create and edit data models and diagrams. They can easily collaborate, make changes, and provide feedback, all within the same document.
Advantages:
- Easy collaboration with team members in real-time.
- Intuitive interface for creating various types of diagrams.
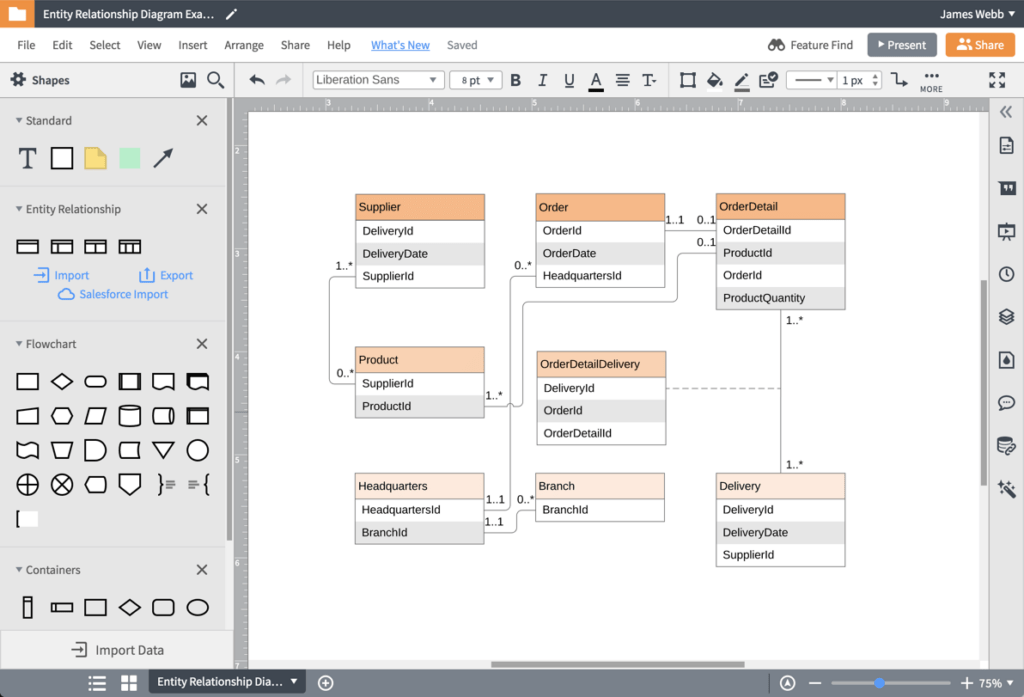
Conclusion
Choosing the right data modelling tool depends on the specific needs and requirements of your data analytics projects. Consider factors such as the scale of your project, integration with existing systems, and the level of collaboration required. By evaluating the features and advantages of each tool, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your data modelling objectives. Remember, the effectiveness of your data models is crucial for accurate analysis and informed decision-making.